In the UK and Europe, nicotine-containing products are legalised under a strict set of regulations and legislation known as TPD and TRPR (the UK equivalent). There are about 6.9 million adults in the UK who are smokers and although these figures are going down, there are still 6.9 million people who are harmfully smoking nicotine. As of 2021, there are around 2.7 million adult vapers in the UK and just half of those have lowered their nicotine strength since starting. What is it about nicotine that has the nation hooked?
What is Nicotine?
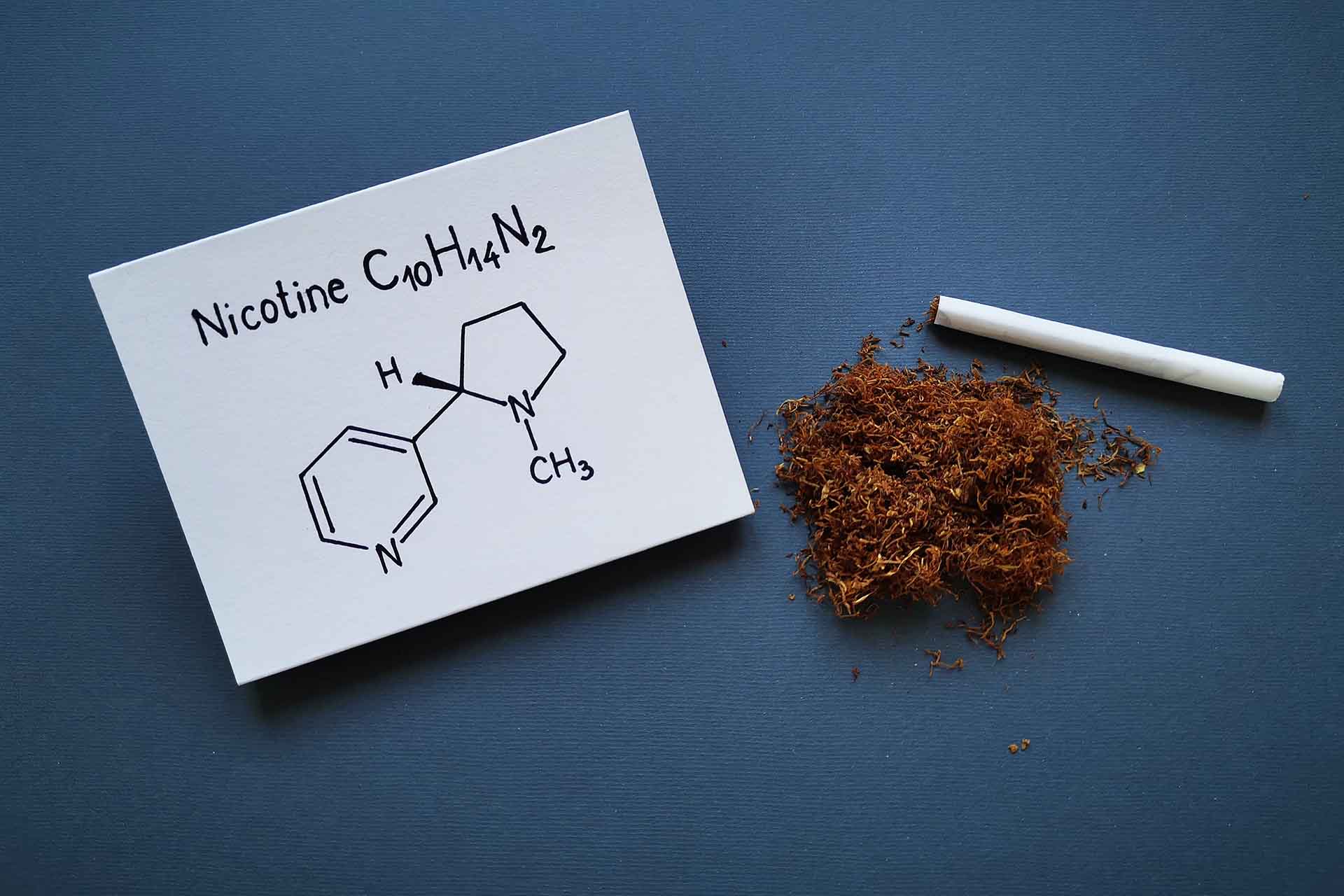
Nicotine is an addictive drug derived from the tobacco plant but also can be found (in much lower dosages) in some foods such as potatoes, tomatoes, and aubergines.
The tobacco plant originated from America before being introduced into Europe. In the 1700s the tobacco industry flourished and exploded in 1880 when mass-produced cigarettes became much easier to produce. But by the end of the 19th century, US lawmakers began to realise the harmful effects of nicotine and laws were passed from selling nicotine to minors.
It's often demonised due to its presence in cigarettes, however, nicotine itself is actually fairly safe. The average cigarette contains 7-14mg of nicotine, of which much of that is not inhaled, and it's estimated that it would perhaps take 500mg to be fatal to an adult making the likelihood of lethal cases of nicotine poisoning low. Even still, it took until 1994 for the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to officially recognise nicotine as a drug that produced dependency.

Why do they worry about nicotine use?
Does nicotine cause cancer? It's a common thought amongst those who first hear about nicotine, and in short, no. The correlation between nicotine and cancers is due to the method of taking nicotine ‚– smoking. Cigarettes have thousands of harmful chemicals that are proven to have links to a wide variety of cancers, but nicotine is not one of them.
Nicotine works by binding to receptors in our nervous system to release “happy chemicals' that create the nicotine buzz. Unfortunately, repeated use of nicotine can train your brain to release less of the chemical acetylcholine that usually does the job of releasing the happy chemical dopamine, effectively taking over the role. This means that your brain can become dependant on nicotine for giving you a buzz of happy chemicals.
It can also create a variety of harmful side effects throughout the body, especially when taken in conjunction with cigarette smoking; the act of smoking itself is extremely harmful. Tie in the withdrawal symptoms once you try to cut out nicotine, it's obvious why becoming addicted to nicotine is worrying.
Although it's important to note, once you cut nicotine out completely, your brain does start producing acetylcholine normally again.
Why is nicotine so addictive?
As mentioned earlier, the problem with nicotine is that it binds to receptors in our brain, which then can become dependent on it for a pleasurable buzz. Due to this, when you take the nicotine away, the psychological side effects of withdrawal are higher than the body's side effects. No one wants to feel down, anxious, irritable, or filled with a craving you don't want to cave into. So those addicted to nicotine find it hard to go cold turkey. Finding an alternative or a way to ease those addicted to nicotine and smoking, can help curb the habit.

Breaking the cycle ‚– is vaping nicotine safer?
Over the last few years, liquid nicotine has been found to be a less harmful replacement for cigarette smoking, as its not classed as carcinogenic nor is cancer-causing. E-Cigarettes atomise the nicotine by applying heat without the harmful oxidative effects of burning. The NHS also noted that E-Cigarettes and liquid nicotine is less harmful and has helped many smokers quit. But it is prudent to note that it is still a highly addictive chemical with side effects, which is why vaping is mainly used by those looking to quit smoking.
Alternatives to nicotine
Recently, CBD has been touted by some as an alternative to nicotine for vaping. CBD (Cannabidiol) is a non-addictive chemical that many say helps promote calm. Some have even claimed that it helps curb tobacco cravings making it especially useful for those looking to quit smoking or lower their nicotine consumption.
A study in 2015 looked at the use of CBD against addictive behaviours, one such being tobacco-related addictive behaviours. There were 24 smokers in the study who aimed to stop smoking, with groups receiving a CBD inhaler or a placebo inhaler. They were told to use the inhaler when they had the urge to smoke. After a two week follow-up, it was found that there was a significant reduction in the number of cigarettes smoked in the CBD inhaler group (40%) during the week of treatment.
Whether you're looking to quit smoking, or looking to lower your nicotine strength, we hope this has provided you with a little more insight into nicotine and why you should want to quit. At Pod Salt, our goal is to help you quit and with vaping, the path becomes much easier. With vaping, you are able to not only switch to a less harmful alternative, but the nature of vaping allows you to be able to tailor your vape to your needs. Are you looking to lower your nicotine intake? Let us know what you've found to help curb the cravings.



